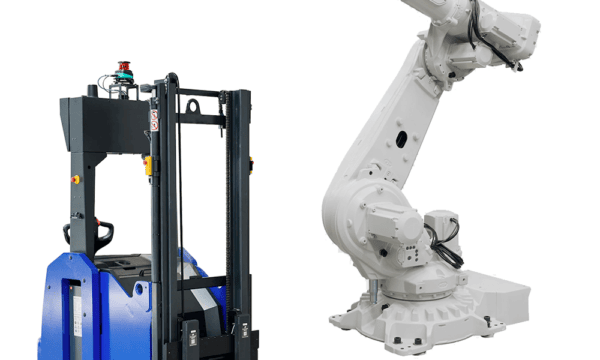
Articulated Industrial Robots are characterized by a series of interconnected joints resembling a human arm, called axes.
These axes, typically revolute or rotary, allow for multi-axis movement, providing the robot with a high degree of flexibility and precision in performing various tasks. These robots come in various sizes and formats, meaning they can be designed for various applications such as pick-and-place, quality control inspection, sorting and much more depending on the type of end-tool. The end-tool can include tools, grippers, and/or sensors depending on the operational need.
